
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
YOUR LATEST ISSUE ABOUT MRCP PACES IS HERE!
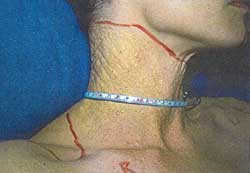
Look at this lady and proceed.( Skin Station )
Discussion:
I still remember when I sat for MRCP PACES 2 years ago, this question was never in the list of topics I studied. I always think that this condition is rare and will never come out in MRCP PACES examination. Recently, my friend took her MRCP PACES in the UK and told me that she got this case and failed badly. Remember that this case is a hot short case in MRCP PACES although you may not have seen it so far. Yes, you notice loose 'chicken skin' appearance of skin.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is hereditary disorder in which the elastic fibres that normally occur in the skin, eyes and cardiovascular system gradually become calcified and cause characteristic symptoms in each area. It can be inherited as either autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant. This disease was first described by Jean Darrier in 1896. The skin lesion you notice in patient with pseudoxanthoma elasticum is always described as papules or 'chicken skin'. The first place you will find is always on the sides or the back of the neck. If you notice this, show to examiners that you anticipate you can find the similar skin lesion at the following sites,
![]() antecubital fossa,
antecubital fossa,
![]() axilla,
axilla,
![]() groin,
groin,
![]() periumbilical region,
periumbilical region,
However, you must always remember that pseudoxanthoma elasticum is a systemic disease involving organs where you can find elastic fibres, therefore tell the examiners you are interested to do the following,
![]() check the fundus for angiod streaks or peau de orange, however remember that there are other causes of angiod streaks!!
check the fundus for angiod streaks or peau de orange, however remember that there are other causes of angiod streaks!!
![]() check for peripheral pulses, due to calcification, there is possibility of vessels narrowing, therefore patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum are prone to get intermittent claudication,angina and heart attack ( due to coronary artery narrowing), anyway remember too that you might get mitral valve prolapse in pseudoxanthomata elasticum,
check for peripheral pulses, due to calcification, there is possibility of vessels narrowing, therefore patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum are prone to get intermittent claudication,angina and heart attack ( due to coronary artery narrowing), anyway remember too that you might get mitral valve prolapse in pseudoxanthomata elasticum,
![]() ask about family history of similar problems,
ask about family history of similar problems,
![]() ask about history of previous gastrointestinal bleeding or uterine bleeding in female patients,
ask about history of previous gastrointestinal bleeding or uterine bleeding in female patients,
OK, I think you will pass this station if you do the above steps while examining a patient with pseudoxanthomata elasticum. Anyway, remember that to confirm the diagnosis, you need a skin biosy. The Kossa stain will reveal staining of calcified elastic tissue.
Diagnosis: This lady has pseudoxanthomata elasticum.
Common questions examiners would ask you,
1) What causes loss of vision in this patient?
2) How do you manage this patient?
3) What are the complications assocaited with pseudoxanthomata elasticum?
Extra points:
| Case ID:2 | Created: 24 December 2007 |
Interesting Images in Clinical Medicine

Case Summary:
This gentleman presents with shortness of breath. What is the diagnosis? Start your discussion with other PassPACES users in our Forum!
To see previous issues, click here! To send a quick comment, click here!