
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
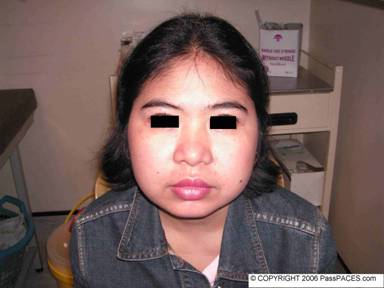
Look at this patient and what do you think about her?
Discussion:
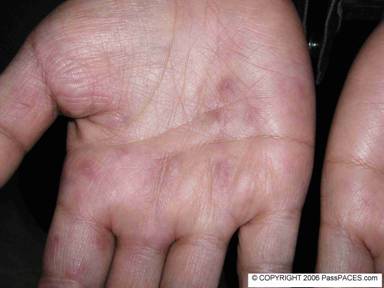
As discussed in previous issues, Cushing’s syndrome is a popular question in MRCP PACES, this lady has a classical moon-like facies. You must look for other relevant clinical signs such as buffalo hump, hirsutism, suprclavicular fat pad. Look for purplish striae, proximal myopathy, spine tenderness and suggest to examiners that you would like to check for BP, urine for glucose and visual field. ( it is rather uncommon for patient to have Cushing’s disease and bitemporal hemianopia because in Cushing’s disease ,the tumour is usually a mircoadenoma). If you look hard, this lady has multiple vasculitic rash over her hands. In MRCP examination, it is not enough for you to get the diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome only. In view of the vasculitic rash over her hands, you must look for other clues to suggest the possible underlying diagnosis for this lady that leads her to be on long-term steroid.
The commonest cause for vasculitic rash is autoimmune disease and this lady is actually having lupus nephritis and on long-term steroid. Suggest to examiners that you want to look for other signs of lupus.
Conclusion:
This lady has Cushing's syndrome secondary to long term steroid ingestion due to lupus nephritis.
Extra points:
- Tests to confirm the presence of Cushing’s syndrome are 24-hour urinary free cortisol and overnight dexamethasone test.
- Further tests to find out the underlying etiology include plasma ACTH level, high dose dexamethasone test, CXR, ultrasound/CT abdomen and sometimes inferior petrosal sinus sampling for ACTH level.
| Case ID: 2 | Created: 1 June 2006 |
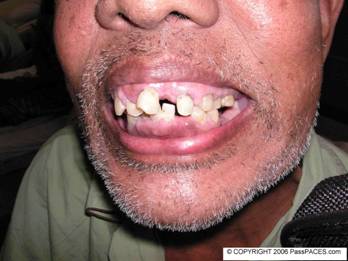
Kindly examine this gentleman’s abdomen.
Discussion:
A common finding in a patient with transplanted kidney but always missed by candidates. This gentleman has a superficial right lumbar mass with a scar. The mass is dull on percussion and there is an AVF over his right wrist. There is no ballotable kidney. Actually this gentleman develops gum hypertrophy due to cyclosporin. A lot of candidates pick up the clinical signs of a transplanted kidney but unfortunately majority of them do not examine further to look hard for side effects of long term immunosuppressants such as signs of Cushing’s syndrome ( due to prednisolone), fine tremor, gum hypertrophy, hypertension (BP), diabetes (urine for sugar) and hypertrichosis (such as in this case) due to cyclosporin and jaundice ( side effect of Azathioprine).
A common question examiners would ask you is ways for you to assess whether the transplanted kidney is functioning well or not, you can suggest the following:
![]() look at the patient’s 24-hours urine volume, good volume suggests good function,
look at the patient’s 24-hours urine volume, good volume suggests good function,
![]() tell examiners whether the transplanted kidney is tender on palpation, if not tender most probably it is functioning well,( although current immunosuppresants make this unlikely to happen even patients have rejection, this sign is a classical sign we were taught in medical school long time ago!)
tell examiners whether the transplanted kidney is tender on palpation, if not tender most probably it is functioning well,( although current immunosuppresants make this unlikely to happen even patients have rejection, this sign is a classical sign we were taught in medical school long time ago!)
![]() auscultate for renal bruit at the transplanted kidney, long term complication of a transplanted kidney is artery stenosis,
auscultate for renal bruit at the transplanted kidney, long term complication of a transplanted kidney is artery stenosis,
![]() look for any recent punctum wound at the AVF, if no recent wound, this implies that patient is not dependent on haemodialysis, therefore the transplanted kidney must be functioning well.
look for any recent punctum wound at the AVF, if no recent wound, this implies that patient is not dependent on haemodialysis, therefore the transplanted kidney must be functioning well.
Conclusion:
This gentleman has a transplanted kidney and on cyclosporin, predisolone and azathioprine and he develops gum hypertrophy, hypertension due to the drugs.
Extra points:
Common side-effects and precautions for immunosuppresants are as follows:
- Cyclosporine- nephrotoxity, hypertension, tremor, gum hypertrophy, hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, weight gain, diabetes mellitus, acne, hypomagnesaeimia. Grapefruit juice and Mediterranean oranges and Sun Drop, a citrus soda, contain bergamottin which enhances the effect of cyclosporine, increasing the level of the drug in circulation. St. John's wort reduces the concentration of cyclosporine rendering it less effective.
- Azathioprine- bone marrow suppression, cholestatic jaundice, GIT upset. Azathioprine can cause irreversible bone marrow failure for those with a particular polymorphism of the TPMT gene. GlaxoSmithKline has a predictive DNA test for this type of problem.
- Prednisolone- Cushing’s syndrome and its complications.
- Mychophenolate-GIT upset, headache, bone marrow suppression.
Other common causes of gum hypertrophy include acute myeloid leukemia, scurvy, medications such as cyclosporine, calcium channel blocker especially nifidipine and phenytoin.
To see previous issues, click here! To send a quick comment, use our shoutbox, click here!
Source:
1) Handbook of Kidney Transplantation, Gabrieal M. Danovitch
(Last modified: 22 October 2006)